

Hospital rates for outpatient surgery paid by workers compensation vary significantly across states, with those states with fixed fee schedules having lower surgery costs for injured workers.
Workers comp costs for injured worker surgery also vary a great deal from Medicare rates for common procedures, reports the Workers Compensation Research Institute (WCRI) in a new study, “Hospital Outpatient Payment Index: Interstate Variations and Policy Analysis, 5th Edition,” which looks at 33 states representing 87 percent of the workers comp benefits paid in the country.
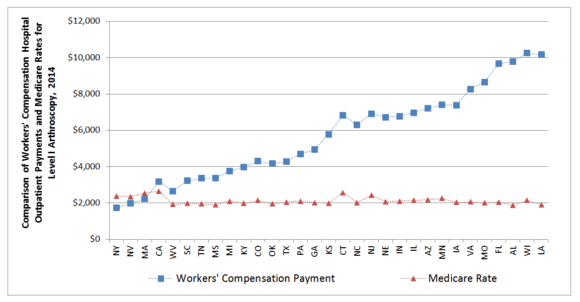
The report found that hospital outpatient payments per surgical episode varied significantly across states, ranging from 69 percent below the study-state median in New York to 142 percent above the study-state median in Alabama in 2014, according to Dr. Olesya Fomenko, co-author of the study and economist at WCRI.
The variation in the difference between average workers comp payments and Medicare rates for a common group of procedures across states was even greater—reaching as low as 27 percent ($631) below Medicare in New York and as much as 430 percent ($8,244) above Medicare in Louisiana.
Ramona Tanabe, executive vice president and counsel at WCRI, said inclusion of the Medicare payment data offers an additional benchmark that may help states better understand their hospital payments.
 Major findings from the study include:
Major findings from the study include:
WCRI’s hospital outpatient payment indices compare payments (per surgical episode) for common outpatient surgeries under workers comp from state to state for each study year and the trends within each state from 2005 to 2014.
The analysis captures payments for services provided and billed by hospitals, and it excludes professional services billed by nonhospital medical providers (such as physicians, physical therapists and chiropractors) as well as transactions for durable medical equipment and pharmaceuticals billed by providers other than hospitals. The analysis also excludes payments made to ambulatory surgery centers.
The 33 states included in this study are Alabama, Arizona, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, Nevada, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Oregon, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, West Virginia and Wisconsin. The 2014 workers comp and Medicare comparison is conducted for 31 states.
Source: Workers Compensation Research Institute (WCRI)